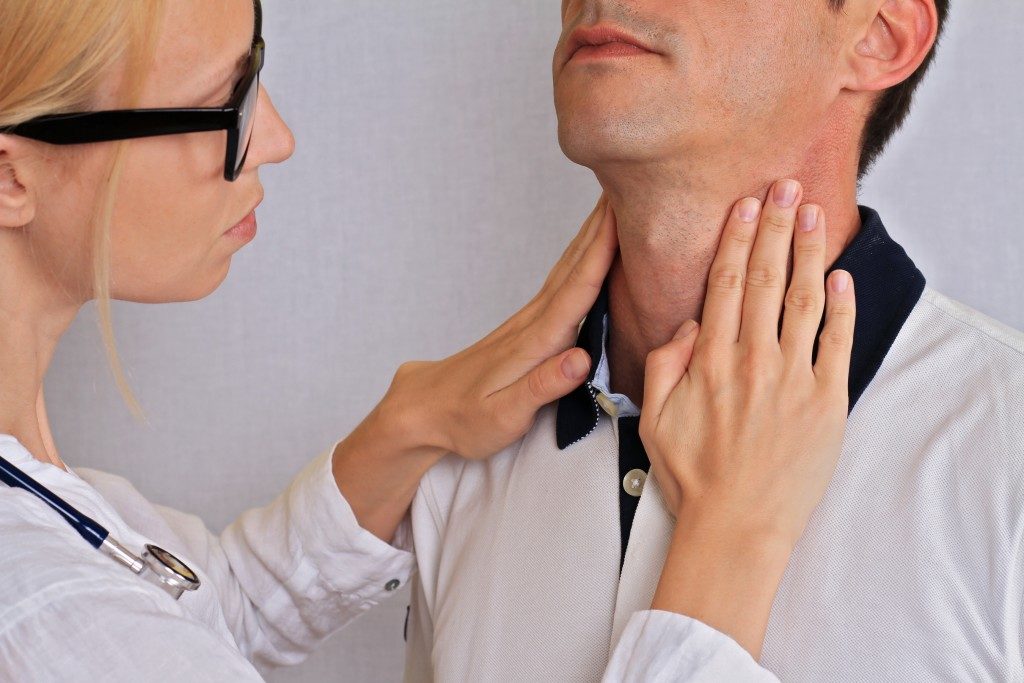
Also known as an overactive thyroid condition, hyperthyroidism is when the thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in your neck that produces two main hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The gland regulates your metabolism and helps control your body temperature, among other essential functions.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), in the United States, about 1.2% of people have hyperthyroidism.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
There are many causes of hyperthyroidism. Some of them are:
- Grave’s disease – An autoimmune disorder, Grave’s disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. With this illness, your thyroid is stimulated to produce too much thyroxine by antibodies created by your immune system.
- Overactive thyroid nodules – This cause for hyperthyroidism occurs when the lumps in your thyroid – called thyroid nodules – become overactive and produce too much thyroxine. The thyroid nodules themselves are common and usually noncancerous.
- Thyroiditis – This is the inflammation of your thyroid gland. When your thyroid gland becomes inflamed, it causes stored thyroid hormones to leak out of your thyroid gland and into your bloodstream.
- Too much iodine – Your thyroid needs iodine to make thyroid hormones. The amount of iodine that you consume affects the amount of thyroid hormone that your thyroid makes. When you consume too much iodine, you could be overstimulating your thyroid to make too much of the thyroid hormone.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
 Hyperthyroidism may be difficult to diagnose since it can mimic other health problems. It also has a wide range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. These symptoms include but are not limited to the following:
Hyperthyroidism may be difficult to diagnose since it can mimic other health problems. It also has a wide range of symptoms that can vary from person to person. These symptoms include but are not limited to the following:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Unintentional weight loss
- Heart palpitations
- Increased appetite
- Irritability
- Nervousness
- Tremors in your hands and fingers
- Changes in menstrual patterns
- Weakness
- Itching
- Fine, brittle hair
- Hair loss
- Difficulty sleeping
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breast development in men
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Thinning skin
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
Older adults who have hyperthyroidism are more likely to either have no signs or symptoms of the illness or have subtle ones, such as heat intolerance or a tendency to become tired easily.
Treatment for Hyperthyroidism
There are several ways to effectively manage your thyroid, Provo specialists say. The best approach for you depends on your physical condition and age, as well as the underlying cause of your hyperthyroidism and its severity. Possible treatments include the following:
- Anti-thyroid medications – These medications prevent your thyroid gland from producing too many hormones. Symptoms start to improve within several weeks to months; however, this treatment typically continues for at least a year.
- Radioactive iodine – Radioactive iodine is absorbed by your thyroid gland, causing it to shrink. Your symptoms will usually subside within several months. Any excess radioactive iodine will disappear from your body in weeks.
- Beta-blockers – While these drugs are usually used to treat high blood pressure, they can also be used to ease the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as tremors, heart palpitations, and rapid heart rate.
Getting treatment for hyperthyroidism as early as possible is important no matter what the underlying cause. If you suspect that you have hyperthyroidism, go to a doctor as soon as you can.