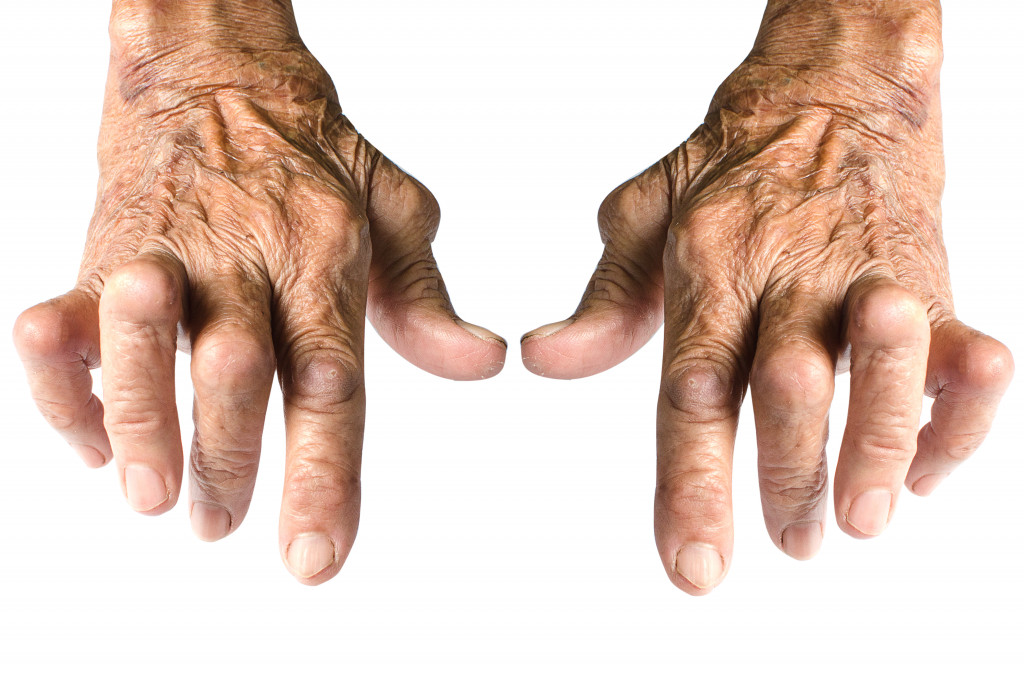
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic joint inflammation and pain.
- RA is diagnosed based on symptoms, blood tests, and imaging to prevent joint damage.
- Genetics, age, gender, lifestyle factors, and environmental factors can increase the risk of developing RA.
- Treatments for RA include massage, exercise, medications, and surgery.
- Working with your doctor to determine the best treatment for you is essential for managing RA effectively.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder that causes chronic joint inflammation and pain. It affects millions worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with RA, you may be curious about what it is, how it is diagnosed, and what treatment options are available.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder, which means the immune system attacks healthy tissue in the body, mistaking it for a foreign substance. In the case of RA, the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Over time, this inflammation can lead to joint deformity and damage.
Symptoms of RA usually start with pain and stiffness in the joints, which can worsen over time. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, and weight loss. RA can also affect other body parts, such as the eyes, lungs, and heart.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
If you are experiencing symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and order blood tests to check for markers of inflammation. They may also order imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to look for joint damage.
Rheumatoid arthritis is typically diagnosed based on symptoms, blood tests, and imaging. Getting an early diagnosis and starting treatment as soon as possible is essential to prevent joint damage and improve your quality of life.
Risk Factors
Anyone can gain RA, but some risk factors can increase your likelihood of developing the disorder. Here are some of them:
Genetics
One of the most significant risk factors for RA is genetics. If you have a family member with this condition, your likelihood of developing it is higher than in individuals without a family history. Certain genes, such as HLA-DR4 and HLA-DR1, are associated with an increased risk of developing RA. It is vital to maintain a healthy lifestyle if you have a family history of this condition to reduce the risk of onset.
Age
As people get older, their risk of developing RA increases. While RA can occur at any age, it is most commonly diagnosed in people between 40 and 60. This increase in risk may be due to changes in the immune system, hormonal imbalances, or environmental exposure but specific causes are yet not identified. However, a healthy lifestyle can help reduce this risk irrespective of genetics or age.
Gender
Women are two to three times more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis than men. Estrogen is thought to play a role in the development of RA, which may explain this disparity. However, the reason for this increased risk in women is not entirely clear.
Lifestyle factors
Various lifestyle factors have been found to contribute to the development of RA. For instance, smoking increases the risk of RA, and there’s ample evidence pointing to this. Studies have shown that smoking can worsen the symptoms of RA and reduce the effectiveness of treatment. Obesity is also considered a risk factor contributing to inflammation and joint damage. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing RA.
Environmental Factors
While genetics and lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of RA, environmental factors such as infections, pollution, or occupational exposures may also trigger the onset of RA. Stress can also be considered an environmental factor triggering RA onset or increasing symptom severity.
Treatments
There are various treatments for RA. Here are some of them:

Massage
The pain for those with RA can be reduced by massage. Massage can reduce inflammation, improve joint range of motion, and decrease pain. If you want better blood, consider getting a deep-tissue massage service. This kind of massage can help relax the muscles and reduce joint tension.
Exercise
Exercising regularly is essential for those with RA. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, biking, or yoga can help improve joint flexibility and range of motion while strengthening the muscles around the joints to protect them from further damage. Exercise can also help reduce pain and fatigue.
Medications
Various medications are available to treat RA, from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). These medications can help reduce inflammation, improve mobility, and prevent joint deformity. Your doctor will be able to determine which medication is right for you.
Surgery
Surgery may sometimes be recommended to repair or replace damaged joints. This is usually used as a last resort after other treatment options have been exhausted, and it can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
RA is a chronic and progressive disorder, but with the right treatment plan, you can manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Working with your doctor to determine the best treatment for you is essential for managing your condition effectively.